How Does Kite Work? An In-Depth Look at Kite's Identity and Programmable Permission Architecture
As AI agents gain autonomy in decision making and execution, identity authentication and permission governance become critical to security and scaling. Traditional accounts and API key models struggle to support AI agents that directly interact with funds, contracts, and data. Kite addresses this by embedding behavioral limits, risk controls, and economic settlement into the protocol layer through a three layer identity structure, Programmable Authority, and the SPACE Framework. Each action becomes verifiable and traceable, providing the technical basis for trustworthy AI coordination and machine economies.
This article introduces Kite at a high level, explains why it focuses on AI identity and permission governance, and examines how the three layer identity model, the SPACE Framework, and programmable authorization support the AI task lifecycle and on-chain coordination. By walking through operational logic and technical structure, it helps readers understand how Kite builds infrastructure for reliable AI agents and why this matters for the future agent economy.
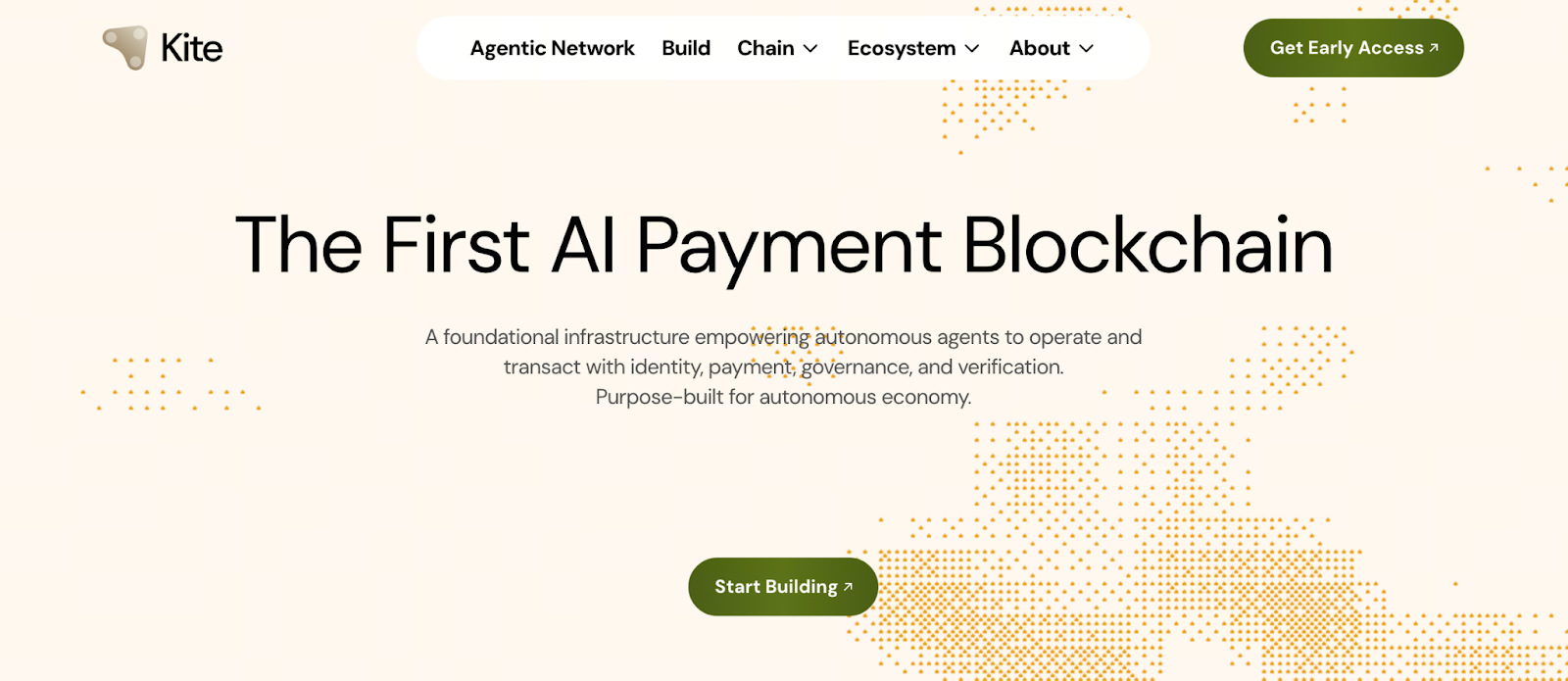
Kite Project Overview
(Source: gokite.ai)
Kite is an EVM compatible Layer 1 blockchain built on proof of stake. Its core goal is to provide AI agents with a verifiable, settlement ready, and coordination friendly on-chain environment. In Kite’s design, an AI agent is not a passive assistant attached to a human account. It is an economic participant with its own on-chain identity and direct asset control. Through native identity systems, programmable rules, and real time settlement, Kite enables AI to pay autonomously, call services, and take part in decentralized coordination, supporting the infrastructure needs of a forming agent economy.
As AI Agents Become Autonomous, Why Identity and Permissions Become the Core Problem
AI is rapidly moving from a support tool into a system that can make and execute decisions. Whether it is an automated trading agent, a research assistant, or a supply chain optimization engine, more AI systems interact directly with funds, contracts, and data. Once an AI can pay or commit to actions, traditional accounts and API key models become fragile. Kite positions agent native economics as the driver for autonomous AI markets and on-chain value exchange.
Earlier AI systems often lacked clear identity boundaries and granular permission management. When something went wrong, responsibility was difficult to trace, and risk could spread before a platform could react. Kite targets this exact weakness by creating a verifiable and governable on-chain identity structure for AI. Under Kite’s design, an AI agent is not simply an extension of a human account. It becomes an independent execution identity that can be audited, governed, and constrained by protocol level rules.
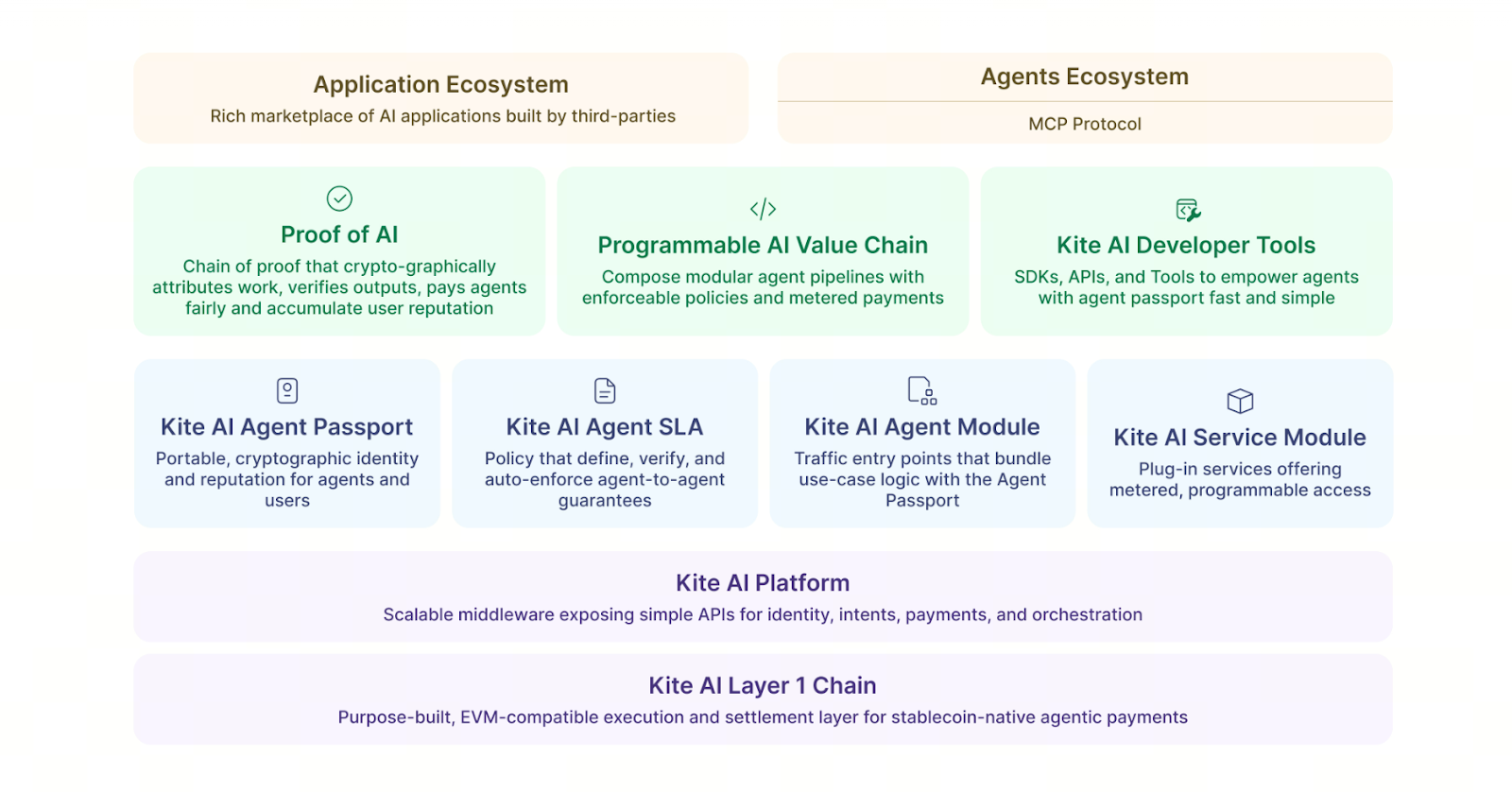
Kite AI Core Operating Mechanism: How the Three Layer Identity Model Works Together
Kite uses a three layer identity design, so every action stays within controlled boundaries. It is not only a technical structure. It is a governance model for permissions.
The top layer is Root Authority, held by the user. This layer sets all agent rules such as budget ceilings, task scope, and authorization logic. Root Authority always retains ultimate control, so the AI cannot exceed human defined permissions.
The middle layer is Delegated Authority, which is the AI agent itself. Each agent has its own wallet and identity and can execute specific tasks, but it cannot change core rules. This allows multiple agents to run in parallel while maintaining clear responsibility boundaries.
The bottom layer is Ephemeral Authority, which is a short-lived identity. It is used for one-time actions such as an API call or a single payment. Once the action is completed, it expires immediately, reducing the risk of long term permission abuse.
(Kite layered architecture overview, source: kite whitepaper)
This layered structure breaks AI permissions into manageable modules and creates an identity system aligned with on-chain security principles.
Key Technical Flow: The Lifecycle of an AI Task in the Kite Ecosystem
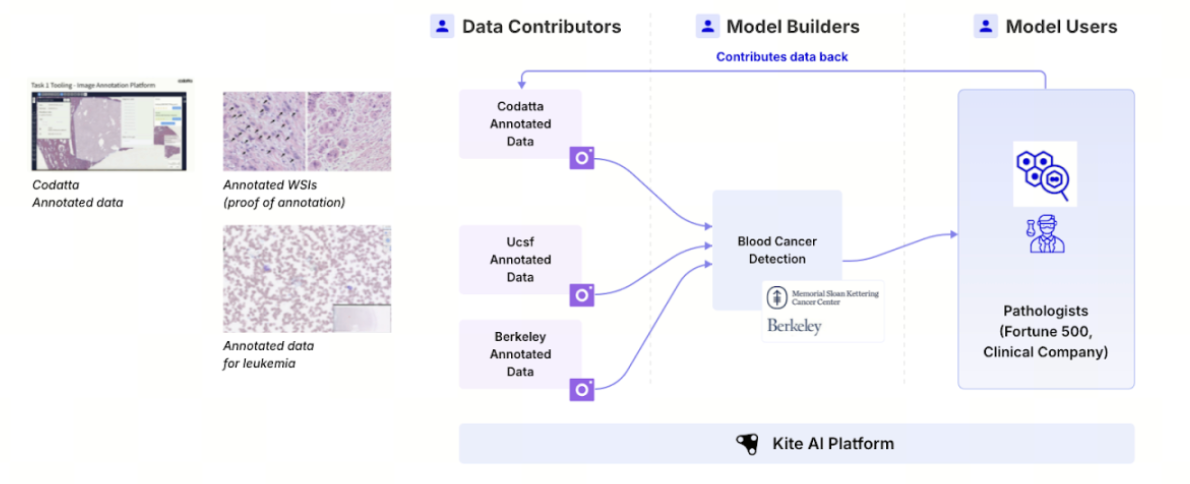
In the Kite ecosystem, an AI task often starts with data access. Codatta, described as the first data module, illustrates how the flow works end to end. Codatta is an on-chain data protocol focused on high value domains such as healthcare, wellness, and embodied intelligence. It aims to provide datasets with verifiable metadata, traceability, and built-in royalty logic.
When an AI agent performs a task, it first uses Kite’s identity system to obtain a verifiable credential, such as an identity passport. Under programmable permission rules, it can then access data. All access and compute activity is recorded on-chain, forming an auditable usage trail. In this process, the AI can obtain high quality data and settle payments without relying on trust, while data providers are paid automatically and retain governance rights. Kite’s coordination logic and smart contracts enforce the workflow.
This closed loop from identity verification to permission control, data invocation, and value settlement forms a standardized AI task lifecycle. It also shows how Kite connects supply and demand through modular architecture to support a sustainable machine economy network.
(Source: GoKiteAI)
Programmable Authority: Writing AI Behavior Control Into the Protocol Layer
In traditional systems, AI constraints are enforced by back end monitoring or manual oversight. Kite shifts control into smart contracts. This means every action is governed by on-chain rules rather than platform policies.
Users can define agent behavior logic such as monthly research budget caps, risk conditions that trigger automatic shutdown, task completion thresholds, and per transaction limits. When an AI attempts an out of scope action, smart contracts block it immediately. This turns risk control from after the fact supervision into upfront constraint. Programmable Authority makes AI behavior auditable and enforceable rules, instead of hidden decisions inside a black box.
SPACE Framework: Kite’s On-Chain Operating Layer and Settlement Engine for AI
The SPACE Framework is Kite’s core execution architecture. It integrates identity verification, payments, authorization, and compliance oriented records. It allows AI agents to run tasks on-chain while ensuring operations remain traceable.
This system supports low cost real time payments, layered identity verification, programmable permission management, complete audit trails, and micropayment settlement. Through SPACE, an AI agent does not only perform actions. It completes a full economic workflow on-chain.
Summary: How Kite Builds Trustworthy AI Agents on-chain
When AI behavior is recorded on-chain, a decentralized reputation system can naturally emerge. Each AI agent can accumulate verifiable history such as task success rates, payment records, and risk control performance. Future AI marketplaces may build credit models from this on-chain history, rewarding high reputation agents with higher value tasks while filtering out low performing agents over time. This can create a self-regulating agent economy.
Kite redesigns how AI identity and responsibility work on-chain. By combining a three layer identity model, programmable authorization, and the SPACE Framework, Kite makes AI actions controllable, verifiable, and auditable. This turns agents from opaque tools into on-chain participants with identity, responsibility, and reputation, laying the foundation for a trustworthy agent economy.
FAQ
How is Kite different from typical AI platforms or blockchains?
Kite is not only an AI tool layer or a smart contract platform. It is designed from the blockchain layer up for AI agents with verifiable identity, on-chain wallets, and programmable permissions. AI becomes an independent economic actor that can pay and execute tasks, while every action is auditable and governable on-chain.
What is the three layer identity model and how does it help users?
The three layers are Root Authority, controlled by the user, Delegated Authority, held by the AI agent, and Ephemeral Authority, used for one-time permissions. This design gives users precise control over AI spending and behavioral boundaries, reduces permission abuse risk, and still enables multiple agents to operate safely in parallel.
What role does the SPACE Framework play in Kite?
The SPACE Framework is Kite’s execution and settlement engine. It integrates identity verification, payment settlement, and permission management. Through SPACE, AI agents can access data, pay for services, and settle micropayments without manual intervention, while maintaining a fully traceable audit record.
Related Articles

What is Fartcoin? All You Need to Know About FARTCOIN

Gold Price Forecast for the Next Five Years: 2026–2030 Trend Outlook and Investment Implications, Could It Reach $6,000?

Crypto Future Profit Calculator: How to Calculate Your Potential Gains

2026 Silver Price Forecast: Bull Market Continuation or High-Level Pullback? In-Depth Analysis of Silver Candlestick Chart

Crypto Futures Calculator: Easily Estimate Your Profits & Risks


