What is ICE Coin?

What Is ICE Coin?
ICE Coin is the native cryptocurrency of the Ice Open Network (ION), a Layer 1 blockchain designed for Web3 applications. On ION, ICE is used to pay transaction fees and participate in ecosystem activities. A Layer 1 blockchain refers to the foundational main chain that processes transactions and hosts decentralized applications (dApps). ION focuses on integrated Web3 solutions, combining digital identity, social networking, content distribution, and data storage. It also features a drag-and-drop dApp generator, making it easier for users to create and deploy decentralized applications.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of ICE Coin (ICE)?
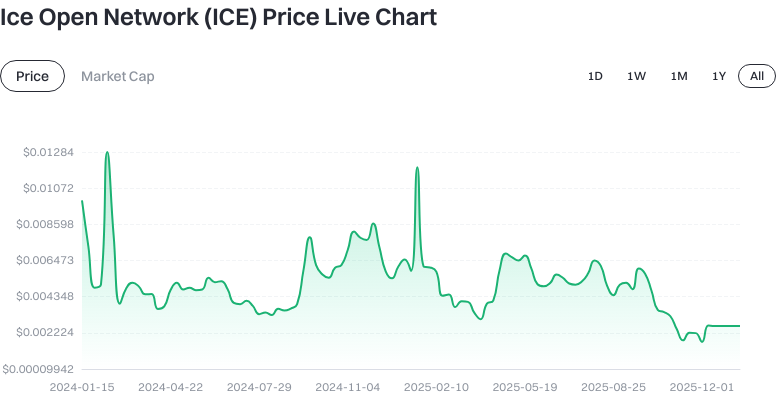
As of 2026-01-16, based on the latest market snapshot on this page: the current price of ICE is $0.002453; its circulating supply is 6,792,780,005.41 ICE. Both total and maximum supply are capped at 21,150,537,435.259998 ICE, indicating a fixed supply limit. The circulating market cap stands at $51,880,787.791072, with a fully diluted valuation at the same amount. ICE’s market dominance is approximately 0.0015%.
View ICE USDT Price
The price has changed -1.43% over the past hour, -3.016% over seven days, and +3.28% over 30 days. Data for 24-hour change and trading volume are not disclosed. These figures provide a snapshot of the current scale and supply structure; actual trading prices may vary due to market liquidity and depth.
Who Created ICE Coin (ICE) and When?
ICE was launched on January 18, 2023 as the native asset of the ION network. It serves as the settlement and incentive token for identity, social, content, and storage services within the ecosystem. Public information primarily highlights product features and functionality; details about the founding team and governance mechanisms are subject to future official disclosures. Investors are encouraged to follow ION’s roadmap and developer community updates.
How Does ICE Coin (ICE) Work?
ION is a Layer 1 blockchain responsible for transaction validation and data storage. When users transfer assets or interact with smart contracts (self-executing programs on the blockchain), they pay network fees in ICE to compensate nodes for computation and storage resources.
ION emphasizes an integrated suite of decentralized services: digital identity enables on-chain account recognition and access control; social interaction and content distribution rely on blockchain-based recording and distribution mechanisms; secure data storage targets encrypted backup and verifiable persistence.
The drag-and-drop dApp generator lets developers visually assemble smart contracts and front ends, reducing barriers to entry. As the native token, ICE handles fee payments, resource metering, and ecosystem incentives. Specifics on consensus mechanism, staking, and node rewards are defined in ION’s technical documentation and on-chain governance decisions.
What Can ICE Coin (ICE) Be Used For?
In identity scenarios, ICE is used as a unit of account for activating or verifying certain on-chain services, supporting privacy controls and access management. Within social apps, ICE can be used for micro-tipping, content payments, or anti-spam fee gates. For content distribution, creators can publish works to the decentralized network and settle storage or bandwidth costs in ICE. Enterprises and independent developers can use the drag-and-drop dApp generator to quickly build internal workflows or user-facing apps—paying for required resources with ICE.
What Wallets and Extensions Are Available in the ICE Coin (ICE) Ecosystem?
The ION ecosystem supports multiple wallet types: browser extension wallets for direct signing and contract interactions in web apps; mobile wallets for on-the-go payments and identity verification; developer tools and SDKs (software development kits) that integrate with the drag-and-drop dApp builder to speed up deployment cycles. Actual available wallets and extensions should be confirmed through ION’s official compatibility lists and version releases—always ensure software comes from trusted sources.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for ICE Coin (ICE)?
Price volatility: Crypto asset prices are highly sensitive to market sentiment and liquidity, resulting in significant short-term swings.
Liquidity and activity: Official metrics indicate that ICE is currently not classified as “active,” so users should pay extra attention to trading depth and overall ecosystem engagement.
Technical and contract risk: Smart contracts may contain vulnerabilities—always audit sources and test with small amounts first.
Regulatory compliance: Cryptocurrency regulations vary by country and region; always comply with local laws and tax requirements.
Custody and private key management: Keeping assets on an exchange involves custodial risk; using a non-custodial wallet means you control your own private keys—always back up securely and beware of phishing or malware threats.
How Do I Buy and Safely Store ICE (ICE) on Gate?
Step 1: Register an account on Gate and complete KYC verification (identity authentication), which enhances account security and meets compliance requirements.
Step 2: Deposit funds. You can buy crypto using fiat or deposit assets like USDT via Gate’s funding page—ensure you select the correct network and confirm receipt.
Step 3: Search for trading pairs. On the spot trading page, search for “ICE” to find available pairs and view live order books and price ranges.
Step 4: Place an order. Choose between a limit order (set your own price and quantity) or a market order (buy instantly at current market price), enter your desired amount, and submit.
Step 5: Withdraw and store assets. After purchase, you can leave ICE in your Gate account or withdraw it to a non-custodial wallet that supports ION. Always verify network compatibility and address format—test withdrawals with a small amount first. Securely back up your recovery phrase and private key; use offline storage whenever possible.
Step 6: Ongoing risk management. Diversify purchases over time, periodically review your portfolio, monitor project announcements or contract upgrades, and follow Gate’s security tips.
How Does ICE Coin (ICE) Compare to Toncoin (TON)?
Project focus: Both are native assets for Layer 1 public blockchains. ICE targets integrated identity, social networking, content distribution, storage services, and features a drag-and-drop dApp generator; TON focuses more on social ecosystem connectivity and high throughput.
Ecosystem maturity: TON has established broader adoption among users and apps; ICE is developing a more productized approach to usability and developer experience—future growth will depend on user acquisition and developer adoption.
Supply & fee structure: ICE has a declared maximum supply cap for settlement and incentives; TON’s monetary policy is governed by on-chain governance and technical updates. Fee models differ—refer to each project’s documentation for details.
Development tools: ICE offers a drag-and-drop dApp generator to lower development barriers; TON invests in parallelization and sharding for performance scaling. Choosing between ecosystems depends on your app requirements, tech stack preference, and target audience.
Summary of ICE Coin (ICE)
ICE powers settlement and incentives across the ION network’s integrated services: digital identity, social interactions, content delivery, and secure storage—made accessible via a visual dApp generator. Current data (as of 2026-01-16) shows a capped supply and established scale, though some real-time indicators are undisclosed; participants should assess liquidity and ecosystem activity before engaging. For newcomers, it’s recommended to buy gradually on Gate, withdraw carefully, safeguard private keys, consult official docs/community updates for long-term value assessment, start small, manage positions prudently, and regularly review your strategy.
FAQ
What Are the Main Use Cases for ICE Coin?
ICE is primarily used within the Injective ecosystem for derivatives trading, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending protocols, and other DeFi scenarios. Holders can stake ICE for governance participation or yield opportunities. It also covers transaction fees and rewards liquidity providers, supporting a complete economic cycle.
How Does ICE Differ from Other Layer 1 Native Tokens?
ICE is Injective’s native asset with a focus on derivatives markets and DeFi infrastructure—whereas Bitcoin or Ethereum serve broader functions as Layer 1 tokens. ICE’s main advantages include low-latency transactions and professional-grade derivatives features tailored for active traders and DeFi users; its ecosystem is more specialized compared to general-purpose blockchains.
What Risks Should ICE Holders Be Aware Of?
Key risks include high market volatility, dependency of ecosystem growth on network adoption rates, as well as leveraged trading risks inherent to derivatives products. Beginners should start with small amounts, learn DeFi fundamentals before increasing exposure, and store large holdings in secure hardware wallets.
How Can I Earn Rewards by Staking ICE?
After purchasing ICE on Gate, you can transfer it to a staking-enabled wallet or DeFi protocol to participate in staking. Staked ICE may earn transaction fee shares, block rewards, or governance tokens depending on protocol terms. Reward rates and lock-up periods vary by protocol—choose options aligned with your risk tolerance.
What Is the Total Supply of ICE Coin? Is There Unlimited Issuance?
ICE has a defined maximum supply limit to prevent inflationary dilution. Its tokenomics include gradually decreasing mining rewards in early stages alongside community governance mechanisms. For detailed economics refer to official documents or check Gate community updates for latest supply information.
Glossary of Key ICE (ICE) Terms
- Circulating Supply: The total number of tokens currently available in the market—used to calculate circulating market cap.
- Maximum Supply: The upper limit of total tokens that can ever be issued—determines long-term scarcity.
- Fully Diluted Valuation: The hypothetical market cap if all possible tokens were in circulation—reflects maximum potential value.
- Market Share: The percentage share this token holds within the total crypto market—measures its overall influence.
- Tokenomics Model: The issuance mechanics, allocation rules, and distribution framework that shape long-term value trends.
- Activity Level: Refers to development progress and community participation—an indicator of project health and lifecycle stage.
Further Reading & References on ICE (ICE)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Docs:
-
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Exploring 8 Major DEX Aggregators: Engines Driving Efficiency and Liquidity in the Crypto Market
