What is Pi Coin?

What Is PiNetwork?
PiNetwork is a cryptocurrency project distinguished by its "mobile mining" feature, with PI serving as its native coin. A native coin refers to the core asset that operates on a project’s proprietary blockchain, used for fee payments, transfers, and in-app settlements. "Mobile mining" enables users to participate in network operations and earn token rewards using mobile devices, rather than relying on energy-intensive mining hardware. The project emphasizes low-barrier participation and community growth, with a capped total supply to limit long-term issuance.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of PiNetwork (PI)?
As of 2026-01-14, PI is priced at $0.209430, with a circulating supply of 8,383,288,945.762151 PI, a total supply of 12,897,367,608.864847 PI, and a maximum supply of 100,000,000,000.000000 PI. The circulating market cap stands at $2,701,095,698.324565, with a fully diluted valuation also at $2,701,095,698.324565 and a market share of 0.079%. The 24-hour trading volume is $1,346,205.908396. Price changes: +0.30% over 1 hour, +1.44% over 24 hours, -1.04% over 7 days, and +2.01% over 30 days.
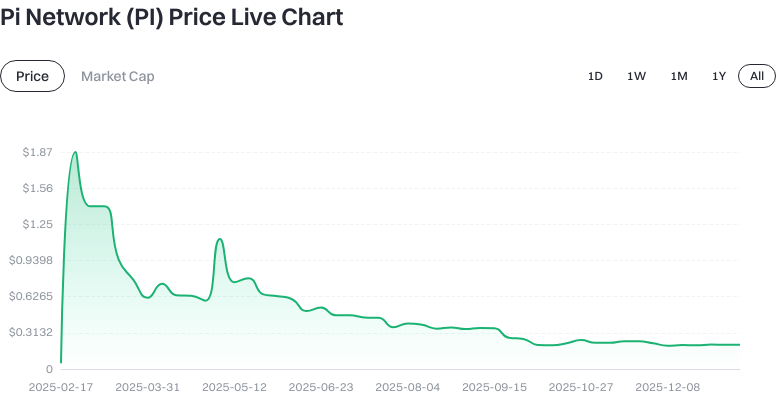
Click to view the latest PI price data
The status is marked as "Inactive," suggesting low trading or on-chain activity and flagging potential liquidity and slippage risks. All data is based on input as of 2026-01-14.
Recent trends show a slight increase over the past 30 days but a decline in the last week—indicating ongoing volatility. The gap between total and maximum supply means future token releases could impact both price and market cap.
Who Created PiNetwork (PI), and When?
PiNetwork's community roots trace back to its early promotion phase focused on mobile mining participation. Its official launch date is documented as 2025-02-19 (input data). According to public sources and the project's whitepaper (accessed on 2026-01-14), PiNetwork was initiated by a team with academic backgrounds advocating for low-energy consensus mechanisms and mass adoption.
Key milestones include the rollout of mobile mining and mainnet development; as the ecosystem matures with application support and wallet features, PI’s use cases and circulation continue to expand.
How Does PiNetwork (PI) Work?
PiNetwork operates through mobile device participation and lightweight nodes forming the network, with its core centered on the consensus mechanism. A consensus mechanism defines how network participants agree on transaction validity. Public materials note that PiNetwork’s approach is inspired by the Federated Byzantine Agreement (FBA) family and leverages trust graphs to minimize energy consumption (source: PiNetwork whitepaper, accessed 2026-01-14).
Mining in this context means earning token rewards according to set rules—designed to incentivize users to maintain network security and engagement. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), which relies on computational power and high energy usage, PiNetwork’s lightweight consensus focuses more on social trust and node collaboration, making mobile participation possible.
What Can You Do With PiNetwork (PI)?
PI primarily facilitates payments and transfers—for example, settling small transactions between friends. Fees and confirmation times depend on network parameters.
It is also used for ecosystem application settlements, such as purchasing digital goods or services in-app, where merchants may accept PI as payment.
Additionally, PI supports community incentives and task rewards—developers can integrate PI as points or access privileges within applications to drive user engagement.
What Wallets and Extensions Are Available in the PiNetwork (PI) Ecosystem?
Wallets are essential for managing assets and private keys. A private key controls access to your assets—whoever holds the private key controls the funds.
- Mobile wallets: Convenient for everyday transfers and balance checks; enable biometric authentication and strong passwords.
- Self-custody wallets: Users manage their own private keys, typically backed up using a mnemonic phrase—a sequence of words that restores your wallet and must be securely stored offline.
- Cold storage: Keeps private keys offline to reduce hacking risk—best suited for long-term holding.
Extensions include price alerts, fee estimators, and transaction export tools to help manage funds and compliance reporting.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for PiNetwork (PI)?
- Liquidity risk: An "Inactive" status may indicate shallow order books and increased slippage—the difference between expected and actual execution prices.
- Supply release and dilution: A discrepancy between current supply and maximum cap suggests that future releases or migrations could affect pricing and valuation.
- Regulatory compliance: Crypto asset trading and taxation requirements vary by jurisdiction—ensure you complete KYC and reporting according to local regulations.
- Private key and account security: Beware of phishing links and fake apps; securely store mnemonic phrases and enable two-factor authentication.
- Technical risks: Uncertainties around mainnet features, ecosystem rollouts, or protocol upgrades may affect functionality or compatibility.
- Market volatility: Short-term price swings can be driven by sentiment or news—set budgets and risk management thresholds accordingly.
How to Buy and Safely Store PiNetwork (PI) on Gate
Step 1: Register and complete identity verification. Go to Gate’s official website or app, create an account, and complete KYC as required for trading limits.
Step 2: Prepare funds. Deposit USDT or use fiat channels to buy USDT on Gate. Monitor fees and deposit times; reserve some funds for transaction fees.
Step 3: Search and place orders. Navigate to spot trading, search for “PI,” select the trading pair, then use either a market order (immediate execution but potential slippage) or a limit order (wait for your set price). Confirm amount and price before submitting.
Step 4: Transfer funds and store securely. After purchase, transfer funds as needed between accounts. For self-custody, withdraw PI to a wallet supporting the PI mainnet standard. Always back up mnemonic phrases offline and enable two-factor authentication plus device encryption.
Step 5: Risk management and recordkeeping. Set price alerts and dollar-cost average your purchases; retain transaction records for reconciliation and compliance reporting. Avoid high leverage or concentrated positions.
How Is PiNetwork (PI) Different from Bitcoin?
- Consensus & energy use: Bitcoin relies on Proof of Work (PoW), requiring computational power and significant energy; PiNetwork uses lightweight consensus suitable for mobile devices with lower energy needs.
- Supply cap: Bitcoin has a maximum supply of 21 million coins; PiNetwork’s maximum supply is set at 100 billion (input data), resulting in different scarcity dynamics.
- Maturity & liquidity: Bitcoin’s ecosystem is more mature with deeper liquidity; PiNetwork is newer—its "Inactive" status suggests possible liquidity limitations.
- Entry barriers: Mining Bitcoin requires specialized equipment; PiNetwork enables easy participation via smartphones for ordinary users.
- Use case focus: Bitcoin is often seen as a store of value or global settlement layer; PiNetwork emphasizes everyday payments, community rewards, and in-app settlements.
Summary of PiNetwork (PI)
PiNetwork lowers entry barriers through mobile mining; PI serves as the native coin for payments and ecosystem settlements with a defined supply cap. Current data shows foundational levels for price, circulation, and market cap—but the "Inactive" status signals potential liquidity and volatility risks. If considering participation, use dollar-cost averaging on Gate with priority for limit orders; maintain transaction records while prioritizing security and compliance. Continuously monitor mainnet progress, ecosystem rollouts, and token release schedules to evaluate long-term value and portfolio allocation dynamically.
FAQ
What Is the Current Price of Pi?
Pi is still in mainnet testing phase—not officially listed on exchanges yet—so there is no official market price. Most online quotes are from unofficial sources or speculative estimates and are not reliable references. It’s best to follow official Pi Network announcements for accurate pricing after the official launch.
How Can I Obtain Pi?
Pi is primarily obtained through mining using the official Pi Network app—simply tap once per day on your phone to start a 24-hour mining cycle. Mining does not drain battery or mobile data; it’s far more eco-friendly than Bitcoin’s PoW mining. New users need an invitation code to register; inviting others boosts your mining speed.
What Are the Risks of Mining Pi?
As an emerging project still in mainnet testing, Pi’s future value is uncertain. Mining rewards decrease as participation grows. Watch out for fake Pi wallets or exchange phishing apps—always download from official channels only. Never pay third parties claiming they can cash out your Pi quickly.
Can I Trade Pi on Gate Once Mainnet Launches?
Once Pi officially launches its mainnet and meets Gate’s listing standards, Gate will evaluate whether to support the project. Follow Gate’s official announcements for updates on listings. Before buying any token on Gate, confirm that it has officially launched with real market liquidity—avoid being misled by speculative projects.
Can I Transfer Mined Pi Tokens to Others?
During mainnet testing, mined Pi tokens are mainly stored in the official wallet; transfer functions are restricted until full mainnet launch. After launch, specific transfer policies will be released by the Pi Network team—on-chain transfers will then be possible via wallet addresses.
Key Terms Related to Pi (PI)
- Mining: The process where users participate in network validation via a mobile app to earn PI rewards.
- Consensus Mechanism: The algorithm through which network nodes agree on transaction validity.
- Wallet: A digital tool used for storing and managing PI coins—including sending and receiving funds.
- Mainnet: The live blockchain network where PI operates independently from test networks.
- Node: A computer participating in maintaining the PI network by validating transactions and supporting the blockchain.
- Blockchain: A distributed ledger technology recording all PI transactions in an immutable history.
Pi (PI) References & Further Reading
-
Official Website/Whitepaper:
-
Development/Docs:
-
Authoritative Media/Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
